C++ 循环¶
在编程中,有时需要执行某个操作 多次 或 n 次。当我们需要重复执行一段语句时,循环就会派上用场。
例如:假设我们要打印 “Hello World” 10 次。这可以通过以下两种方式完成:
手动方法(迭代方法)¶
我们需要手动编写 cout 语句 10 次。如果需要写 20 次,编写时间会更长;想象一下,如果需要写 100 次,那将会非常繁琐。此时,循环发挥了它的作用。
- C++
// C++ 程序演示为什么需要循环
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "Hello World\n";
cout << "Hello World\n";
cout << "Hello World\n";
cout << "Hello World\n";
cout << "Hello World\n";
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
使用循环¶
在循环中,只需要编写一次语句,循环将执行 10 次。计算机编程中的循环是一系列重复执行的指令,直到满足某个条件为止。
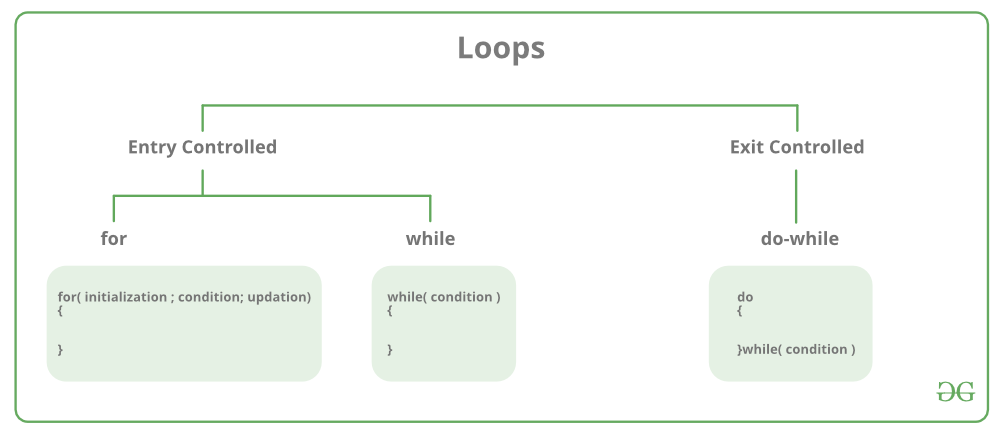
循环的两种主要类型:¶
- 入口控制循环:这种循环在进入循环体之前进行条件判断。
For 循环和While 循环都是入口控制循环。 - 出口控制循环:这种循环在循环体结束后进行条件判断。因此,无论条件是否为真,循环体至少会执行一次。
do-while 循环是出口控制循环。
| S.No. | Loop Type and Description |
|---|---|
| 1. | while loop– 首先检查条件,然后执行循环体。 |
| 2. | for loop– 首先初始化,然后检查条件,执行循环体,更新。 |
| 3. | do-while loop– 首先执行循环体,然后检查条件。 |
For 循环¶
For 循环是一种重复控制结构,允许我们执行指定次数的循环。它使我们能够在一行中完成多步操作。
语法
for (initialization expr; test expr; update expr)
{
// body of the loop
// statements we want to execute
}
语法解释:¶
- 初始化语句:只在 for 循环的开头执行一次。你可以声明多个变量,如
int x = 0, a = 1, b = 2,这些变量仅在循环的范围内有效。 - 条件语句:在每次执行循环体之前进行评估,如果条件为假,则终止执行。
- 更新语句:在循环体执行后进行更新,除非在循环体中使用
break、goto、return或抛出异常来终止循环。
注意事项:¶
- 初始化和递增语句可以执行与条件判断无关的操作,甚至不执行任何操作,但良好的实践是仅执行与循环直接相关的操作。
- 在初始化语句中声明的变量仅在 for 循环的作用域内可见,循环结束后该变量将被释放。
- 不要忘记,在初始化语句中声明的变量以及在条件中检查的变量都可以在循环中被修改。
示例1:
示例2:
for 循环流程图:¶

示例1:
- C++
// C++ program to Demonstrate for loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
cout << "Hello World\n";
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度:O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
示例2:¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[] {40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100};
for (auto element: arr){
cout << element << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(n) n 是数组的大小。
空间复杂度: O(n) n 是数组的大小。
for 循环也可以用以下形式:¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 0, j = 10, k = 20; (i + j + k) < 100;
j++, k--, i += k) {
cout << i << " " << j << " " << k << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
示例隐藏声明的变量:¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 99;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << i << "\t";
}
cout << "\n" << i;
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
但如果你想使用已经声明的变量而不是隐藏它,则不能重新声明该变量。
示例:¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 99;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n" << i;
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
For 循环还可以用于遍历 STL 容器中的元素(例如,Vector)。在这里我们需要使用迭代器。
For Example:¶
- C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
it != v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << "\t";
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(n) n 是 vector 的大小。
空间复杂度: O(n) n 是 vector 的大小。
While 循环¶
在研究 for 循环时,我们已经看到,当循环的迭代次数 已知, 即已知循环体需要执行的次数。while 循环用于在 不知道 循环的确切迭代次数的情况下,基于测试条件终止循环执行。我们已经说明循环主要由三条语句组成 – 初始化表达式、测试表达式和更新表达式。三种循环的语法 – For、while 和 do while 主要在这三条语句的位置上有所不同。
语法:
while 循环流程图:¶
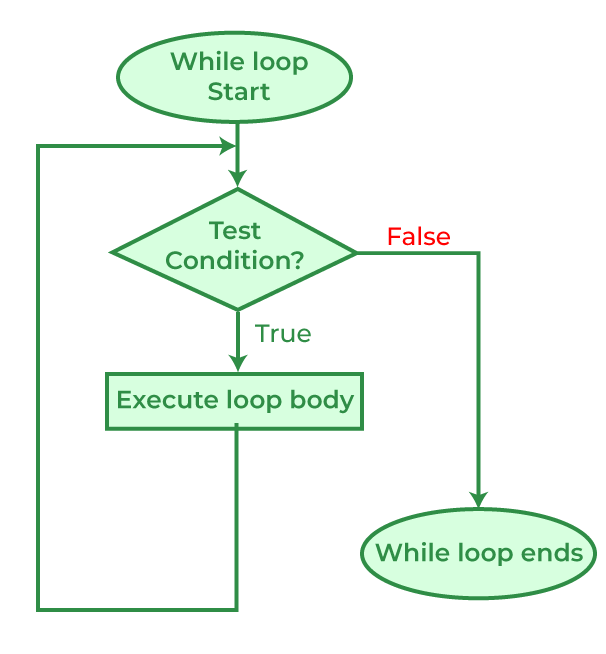
示例:
- C++
// C++ program to Demonstrate while loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// initialization expression
int i = 1;
// test expression
while (i < 6) {
cout << "Hello World\n";
// update expression
i++;
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
其解释与 for 循环相同。
do-while 循环¶
在 do-while 循环中,循环的执行也是根据测试条件终止。与 while 循环的主要区别在于 do-while 循环的条件是在循环体末尾测试的,即 do-while 循环是出口控制的,而另外两个循环是入口控制的。 注意:在 do-while 循环中,循环体将至少执行一次,无论测试条件如何。 语法
initialization expression;
do
{
// statements
update_expression;
} while (test_expression);
注意:请注意循环结束处的分号(“;”)。
do-while 循环流程图:¶
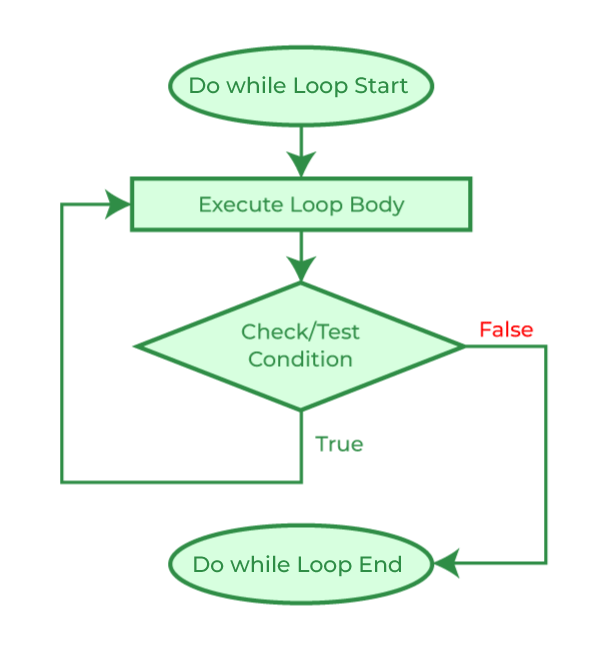
示例:
- C++
// C++ program to Demonstrate do-while loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i = 2; // Initialization expression
do {
// loop body
cout << "Hello World\n";
// update expression
i++;
} while (i < 1); // test expression
return 0;
}
Output
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
在上面的程序中,测试条件 (i < 1) 的结果为假。但由于循环是出口控制的,因此循环体仍将执行一次。
什么是无限循环?¶
无限循环(有时称为无尽循环)是缺少 功能性退出条件 的代码段,从而导致其无限重复。当一个条件始终为真时,就会发生无限循环。通常这是一种错误。
使用 for 循环:¶
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate infinite loops
// using for and while loop
// Uncomment the sections to see the output
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
// This is an infinite for loop as the condition
// expression is blank
for (;;) {
cout << "This loop will run forever.\n";
}
// This is an infinite for loop as the condition
// given in while loop will keep repeating infinitely
/*
while (i != 0)
{
i-- ;
cout << "This loop will run forever.\n";
}
*/
// This is an infinite for loop as the condition
// given in while loop is "true"
/*
while (true)
{
cout << "This loop will run forever.\n";
}
*/
}
输出
Time complexity: O(infinity) as the loop will run forever.
Space complexity: O(1)
Using While loop:¶
- C++
#include <iostream>``using` `namespace` `std;` `int` `main()``{` ` ``while` `(1)`` ``cout << ``"This loop will run forever.\n"``;`` ``return` `0;``}
Output:
时间复杂度: O(∞) 因为循环将永远运行。
空间复杂度: O(1)
使用 while 循环:¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
while (1)
cout << "This loop will run forever.\n";
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(∞) 因为循环将永远运行。
空间复杂度: O(1)
现在让我们看看递减循环。¶
有时我们需要在循环条件下递减一个变量。
使用 for 循环¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for(int i=5;i>=0;i--){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
使用 while 循环¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//first way is to decrement in the condition itself
int i=5;
while(i--){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
//second way is to decrement inside the loop till i is 0
i=5;
while(i){
cout<<i<<" ";
i--;
}
return 0;
}
输出
时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
使用 do-while 循环¶
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i=5;
do{
cout<<i<<" ";
}while(i--);
}
输出
- 时间复杂度: O(1)
空间复杂度: O(1)
- C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// For loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
cout << "For loop: The value of i is: " << i << endl;
}
// While loop
int j = 1;
while (j <= 5) {
cout << "While loop: The value of j is: " << j << endl;
j++;
}
// Do-while loop
int k = 1;
do {
cout << "Do-while loop: The value of k is: " << k << endl;
k++;
} while (k <= 5);
// Range-based for loop
vector<int> myVector = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int element : myVector) {
cout << "Range-based for loop: The value of element is: " << element << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
For loop: The value of i is: 1
For loop: The value of i is: 2
For loop: The value of i is: 3
For loop: The value of i is: 4
For loop: The value of i is: 5
While loop: The value of j is: 1
While loop: The value of j is: 2
While loop: The value of j is: 3
While loop: The value of j is: 4
While loop: The value of j is: 5
Do-while loop: The value of k is: 1
Do-while loop: The value of k is: 2
Do-while loop: The value of k is: 3
Do-while loop: The value of k is: 4
Do-while loop: The value of k is: 5
Range-based for loop: The value of element is: 1
Range-based for loop: The value of element is: 2
Range-based for loop: The value of element is: 3
Range-based for loop: The value of element is: 4
Range-based for loop: The value of element is: 5
- C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// for loop example
cout << "For loop:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << i << endl;
}
// while loop example
cout << "While loop:" << endl;
int j = 0;
while(j < 5) {
cout << j << endl;
j++;
}
// do-while loop example
cout << "Do-while loop:" << endl;
int k = 0;
do {
cout << k << endl;
k++;
} while(k < 5);
return 0;
}
输出
优点:¶
- 高性能:C++ 是一种编译型语言,能够生成高效且高性能的代码。它允许进行底层内存操作和直接访问系统资源,适用于需要高性能的应用程序,如游戏开发、操作系统和科学计算。
- 面向对象编程:C++ 支持面向对象编程,允许开发者编写模块化、可重用且易于维护的代码。它提供了继承、多态、封装和抽象等特性,使代码更易理解和修改。
- 应用范围广泛:C++ 是一种多用途语言,可用于各种应用程序,包括桌面应用、游戏、移动应用、嵌入式系统和 Web 开发。它还广泛用于操作系统、系统软件和设备驱动程序的开发。
- 标准化语言:C++ 是一种标准化语言,ISO(国际标准化组织)维护其规范。这确保了在一个平台上编写的 C++ 代码可以轻松移植到另一个平台,成为跨平台开发的热门选择。
- 庞大的社区和资源:C++ 拥有庞大且活跃的开发者和用户社区,在线上有许多可用资源,包括文档、教程、库和框架。开发者可以轻松找到帮助和支持。
- 与其他语言的互操作性:C++ 可以轻松与其他编程语言(如 C、Python 和 Java)集成,使开发者能够在应用程序中利用不同语言的优势。
总体而言,C++ 是一种强大且灵活的语言,能够为需要创建高性能、可靠和可扩展应用的开发者提供许多优势。
更高级的循环技术¶
重要点¶
- 当循环体执行次数已知时,使用 for 循环。
- 当循环的确切次数未知,但已知循环终止条件时,使用 while 循环。
- 如果代码至少需要执行一次,比如菜单驱动的程序中,使用 do while 循环。