C++中的条件判断¶
在 C++ 中,条件判断(也称为决策控制语句)涉及使用条件语句来根据给定的情况和结果执行特定的代码块。
基本上,在条件判断中,我们会评估条件并决定应执行哪部分代码。它允许选择性地执行代码,对于控制程序的执行流程并使其更加动态化至关重要。
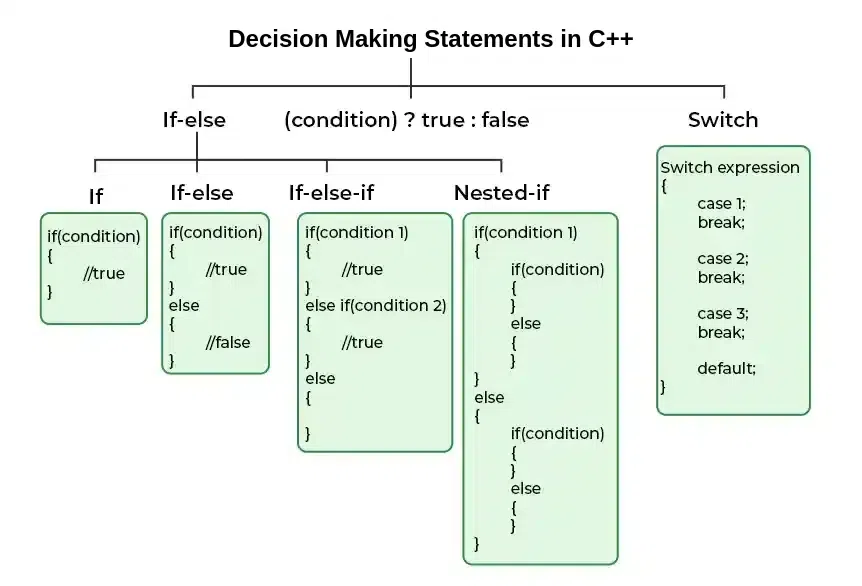
C++中的条件判断语句类型¶
在 C++ 中,提供了以下几种条件判断语句:
- if 语句
- if-else 语句
- if-else-if 语句
- 嵌套 if 语句
- switch 语句
- 条件运算符(三元运算符)
- 跳转语句:
break、continue、goto、return
1. C++ 中的 if 语句¶
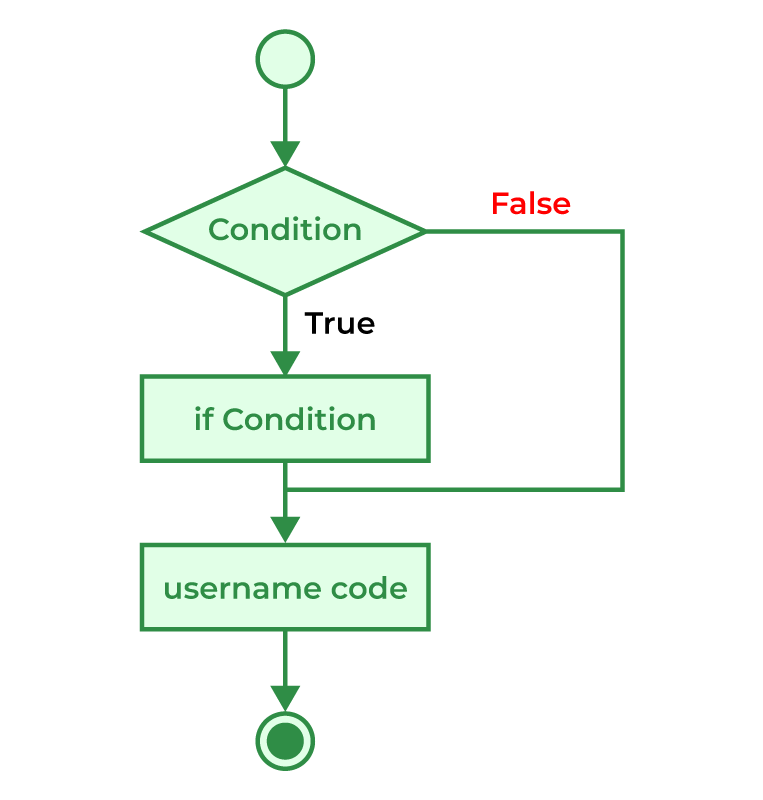
在 C++ 中,if 语句 是最简单的条件判断语句。如果给定条件为真,则允许执行一段代码。只有当条件为真时,if 语句的主体才会被执行。
C++ 中 if 语句的语法¶
这里,如果条件为真,那么 if 代码块中的代码将被执行;否则,将不会执行。
C++ 中 if 语句的流程图¶
C++ 中 if 语句的示例¶
以下示例演示了如何使用 if 语句来判断一个人的年龄是否大于 18。如果条件为真,则表示此人可以投票。
- C++
// C++ program to find if the age of a person id greater
// than 18 or not
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int age = 19;
if (age > 18) {
cout << "allowed to vote" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
2. C++ 中的 if-else 语句¶
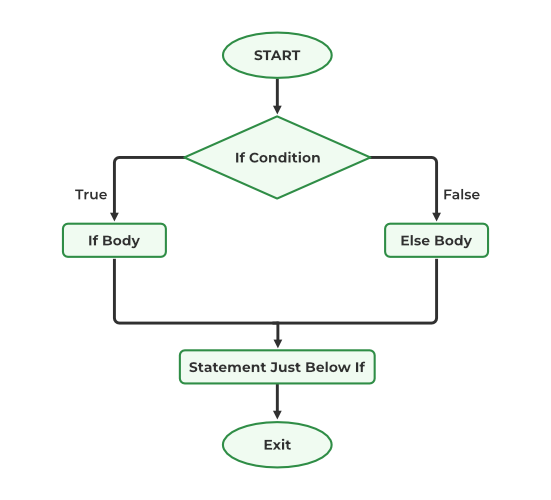
if-else 决策语句允许我们根据给定条件的评估结果做出决策。如果条件为真,则执行 if 代码块中的代码;如果条件为假,则执行 else 代码块中的代码。
C++ 中 if-else 语句的语法¶
if (condition) {
// Code to be executed if the condition is true
}
else {
// Code to be executed if the condition is false
}
C++ 中 if-else 语句的流程图¶
C 语言中的 if-else 示例¶
以下示例演示了如何使用 if-else 语句来判断给定的数字是正数还是非正数
- C++
// C++ program to find if the given number is positive or
// non positive
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num = 5;
// Using if-else to determine if the number is positive
// or non positive
if (num > 0) {
cout << "number is positive." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "number is non-positive." << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
3. C++ 中的 if-else if 梯级语句¶
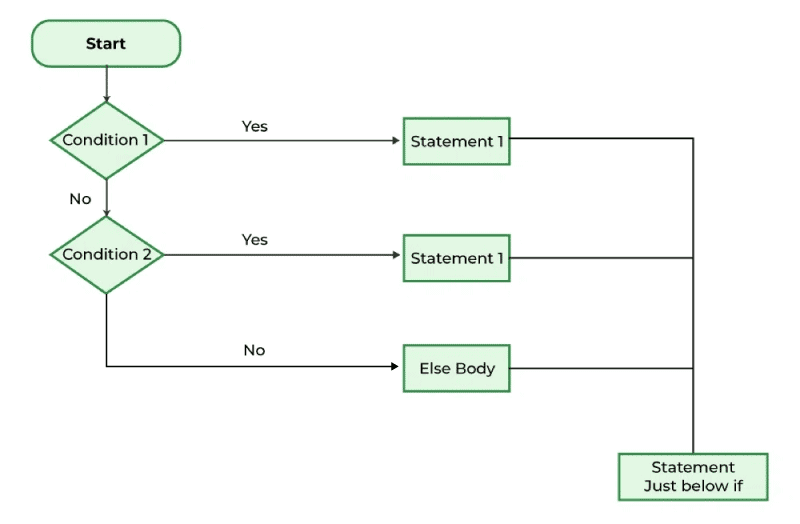
if-else-if 语句允许我们在初始 if 条件之后包含额外的情况。else if 条件只有在前面的条件不为真时才会被检查。而 else 是在所有之前的条件都不为真时执行的语句。如果某个条件为真,则只会执行与该条件关联的代码块。
C++ 中 if-else-if 梯级语句的语法¶
if (condition1) {
// code to be executed if condition1 is true
}
else if (condition2) {
// code to be executed if condition2 is true
}
else {
// code to be executed if both the condition is false
}
我们可以使用多个 else if 语句与 if-else 配对来指定不同的条件。
C++ 中 if-else-if 梯级语句的流程图¶
C++ 中 if-else-if 梯级语句示例¶
以下示例演示了如何使用 if-else-if 梯级语句。在程序中,给定一个年龄,如果年龄小于 13,输出 "child";如果年龄在 13 到 18 之间,输出 "growing stage";否则,输出 "adult"。
- C++
// C++ program to find if the person is child, growing age
// or adult using if else-if ladder
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int age = 18;
// if this condition is true child is printed
if (age < 13) {
cout << "child" << endl;
}
// if above above if statement is not true then we check
// this else if condition if it evalutes to true print
// growing age
else if (age >= 1 and age <= 18) {
cout << "Growing stage" << endl;
}
// if none of above condition is true print adult
else {
cout << "adult" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
4. C++ 中的嵌套 if-else 语句¶
嵌套 if-else 语句 包含一个 if 语句嵌套在另一个 if 语句内部。这种结构允许通过比较多个条件来进行更复杂的选择。在这种语句中,会检查多个条件,然后执行最后一个 if 语句的代码块。
C++ 中嵌套 if-else 语句的语法¶
if (condition1) {
// code to be executed if condition 1 is true
if (condition2) {
// code to be executed when condition 2 is true.
}
else {
// code to be executed if condition1 is true but condition2 is false.
}
}
else {
// code to be executed when condition 1 is false
}
嵌套 if-else 语句的流程图¶
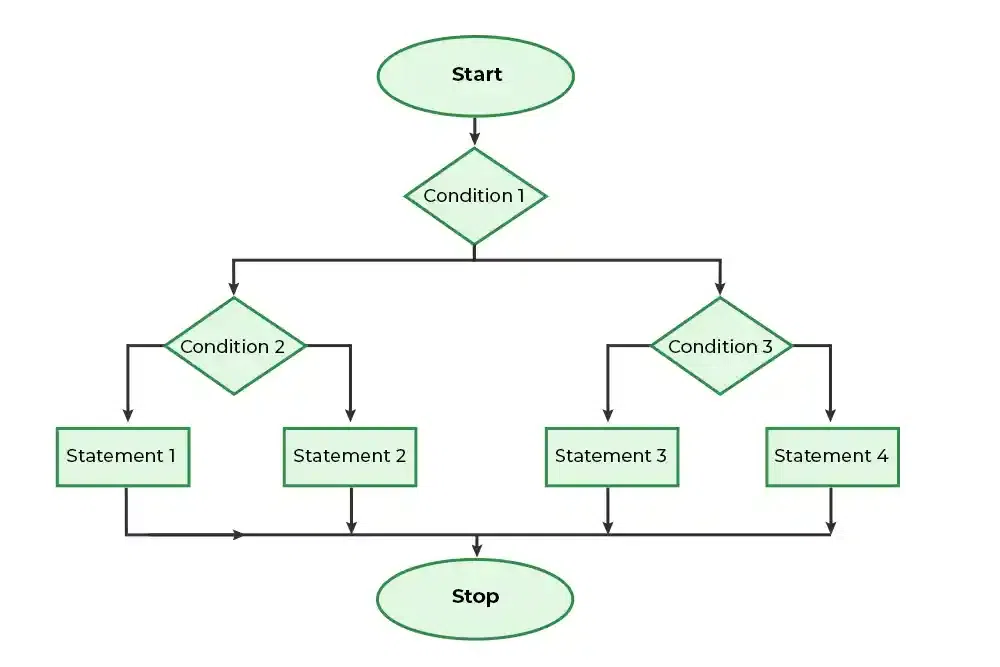
C++ 中嵌套 if-else 语句示例¶
以下示例演示了如何使用嵌套 if-else 语句。在程序中,给定一个数字,我们需要检查这个数字是正数、负数还是零。如果数字是正数,再检查它是偶数还是奇数。
- C++
// C++ program to check if the given number is positive,
// negative or zero if positive then check if it is even or
// odd
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int number = 44;
// to check if number is positive
if (number > 0) {
// to check if the positive number is even or odd
if (number % 2 == 0) {
cout << "positive and even number" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "positive and odd number" << endl;
}
}
// to check if the number is 0
else if (number == 0) {
cout << "the number is zero" << endl;
}
// to check if the number is negative
else {
cout << "the number is negative" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
5. C++ 中的 switch 语句¶
在 C++ 中,switch 语句 在需要根据变量或表达式的值评估多种情况时使用。switch 语句是多个 if 语句或 if-else 梯级语句的替代方案,具有更清晰的结构,更易于处理多个条件。
C++ 中 switch 语句的语法¶
switch (expression) {
case value1:
// code to be executed if the value of expression is value1.
break;
case value2:
// code to be executed if the value of expression is value2.
break;
//…..
default:
// code to be executed if expression doesn't match any case.
}
C++ 中 switch 语句的流程图¶
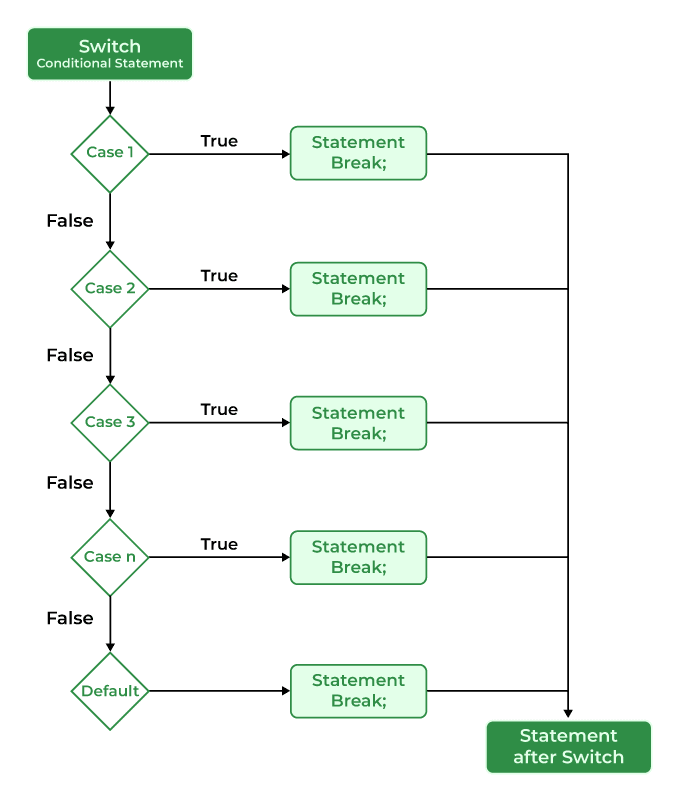
C++ 中 switch 语句的示例¶
下面的示例演示了如何在条件判断中使用 switch 语句。在程序中,给定一个字符,如果输入是 A,则输出 "SDNU",如果输入是 B,则输出 "211Lab",否则输出 "无效输入"。
- C++
// C++ program to use switch case and print certain output
// based on some conditions
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char input = 'B';
switch (input) {
// if the input character is A then print GFG
case 'A':
cout << "SDNU" << endl;
break;
// if the input character is B then print GeeksforGeeks
case 'B':
cout << "211Lab" << endl;
break;
default:
// if th einput character is invalid then print
// invalid input
cout << "无效输入" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output
6. C++ 中的三元运算符 ( ? : )¶
条件运算符 也被称为 三元运算符。它用于编写 C++ 提供的条件操作。? 运算符首先检查给定条件,如果条件为真,则执行第一个表达式,否则执行第二个表达式。它是 C++ 中 if-else 语句的替代方案。
C++ 中三元运算符的语法¶
C++ 中条件运算符(? :)的流程图¶
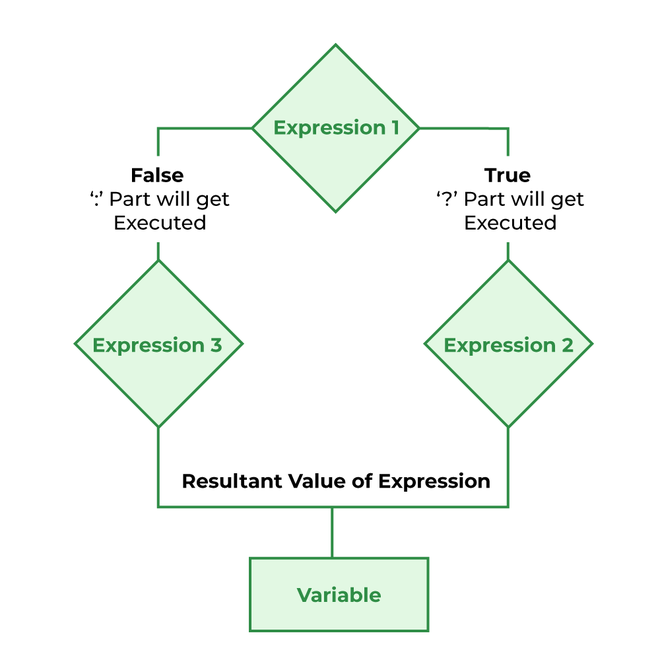
C++ 中三元运算符的示例¶
下面的程序演示了如何使用条件运算符来找出两个数字中的最大值。
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the use of ternary/conditional
// operator to find the max from two numbers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num1 = 10, num2 = 40;
int max;
// if the condition is true then num1 will be printed
// else num2 will printed
max = (num1 > num2) ? num1 : num2;
cout << max;
return 0;
}
输出
7. C++ 中的跳转语句¶
跳转语句用于改变代码的正常执行流程。如果你想在没有任何条件的情况下中断程序的执行,可以使用这些跳转语句。C++ 提供了四种类型的跳转语句。
- break
- continue
- goto
- return
A) break¶
break 是一种控制流语句,用于终止循环和 switch 语句。当遇到 break 语句时,它会将控制权转移到循环之后的语句。
语法
break 语句通常在实际的迭代次数未预先定义时使用,以便根据某些条件终止循环。
break 的流程图
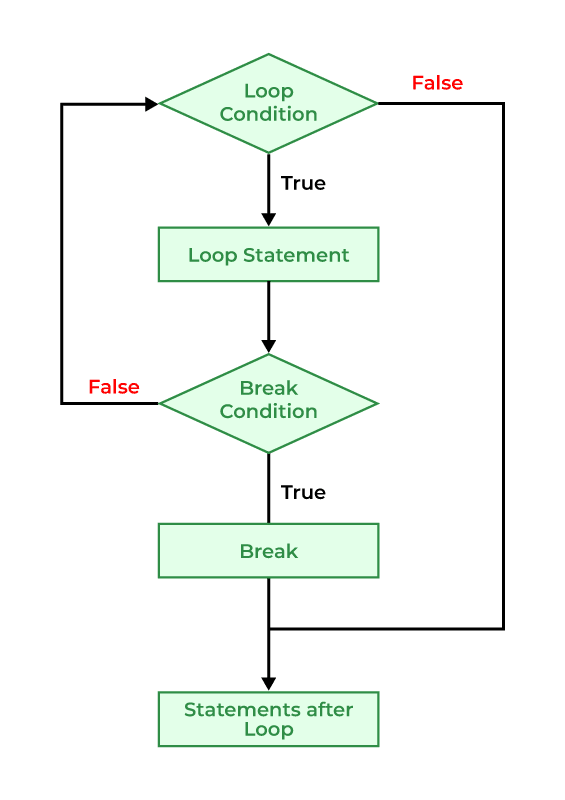
样例 下面的示例演示了如何使用 break 来管理控制流。
- C++
// C++ program to use break statement to break the loop when
// i become 3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// if i become 3 then break the loop and move to
// next statement out of loop
if (i == 3) {
break;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
// next statements
return 0;
}
输出
B) continue¶
continue 语句用于跳过当前迭代的循环体,并从下一次迭代开始。与 break 语句完全终止循环不同,continue 语句只跳过一次迭代,并继续下一次迭代。
语法
continue 的流程图
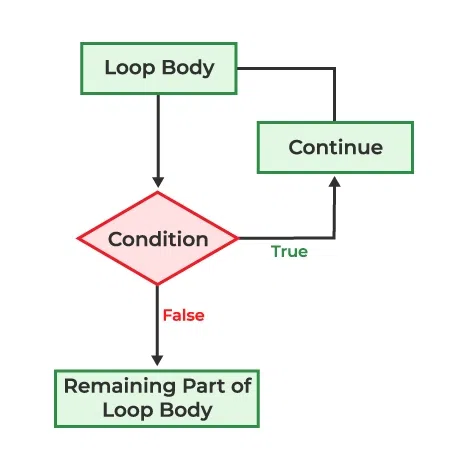
样例 下面的示例演示了如何使用 continue 来管理控制流。
- C++
// C++ program to use continue statement to continue the
// loop when i become 3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// if i become 3 then skip the rest body of loop and
// move next iteration
if (i == 3) {
continue;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出
C) goto¶
它是一种跳转语句,用于将控制权转移到程序的另一部分。它无条件地将控制权转移到标记语句处。
语法
goto 的流程图
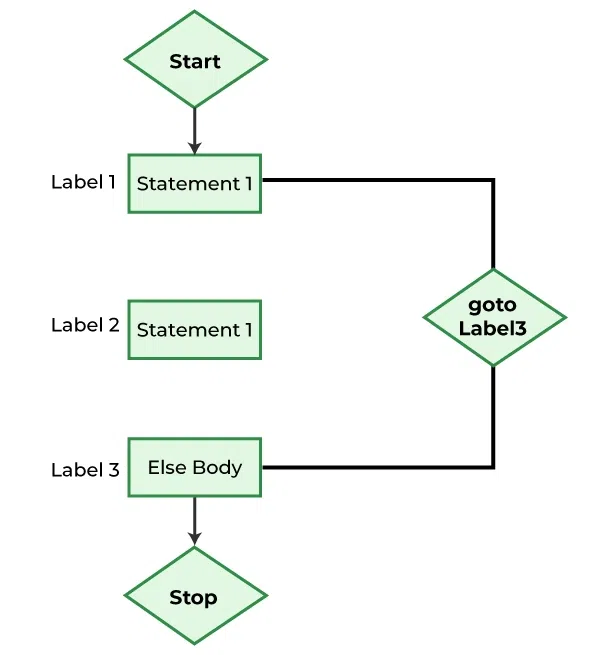
样例
下面的示例演示了如何使用 goto 语句。
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the use of goto statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int age = 17;
if (age < 18) {
goto Noteligible;
}
else {
cout << "You can vote!";
}
Noteligible:
cout << "You are not eligible to vote!\n";
return 0;
}
输出
注意:在现代编程实践中,通常避免使用
goto,因为它可能会影响代码的可读性,并使代码容易出错,尽管它仍然有效并偶尔使用。
D) return¶
return 语句用于立即退出函数,并可选择性地返回一个值给调用函数。它将控制权返回到调用该函数的位置,如果是在 main 函数中,则标志着程序执行的结束。基本上,return 是一种将结果传回给调用函数的机制。
语法
return 的流程图
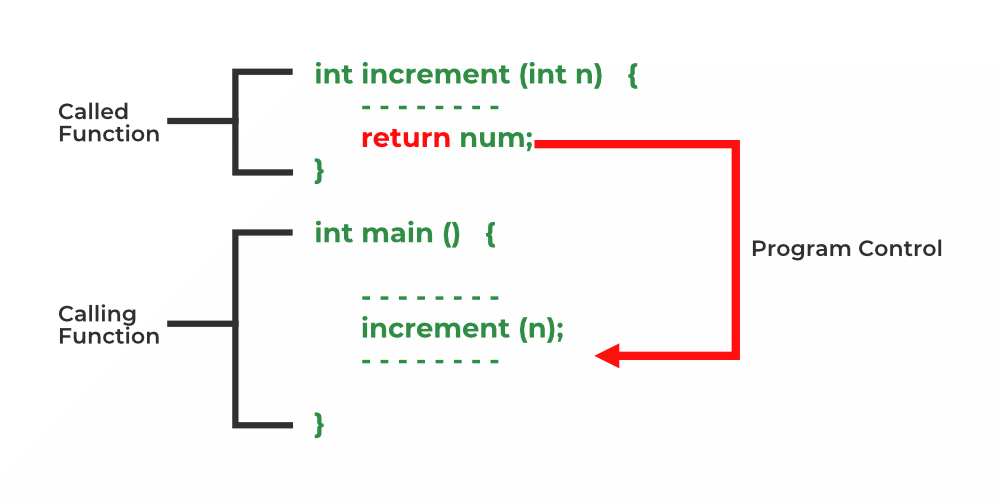
样例
下面的示例演示了如何使用 return 语句从函数中返回一个值。
- C++
// C++ program to use return statement to return the sum
// calculated by a function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to add two numbers and returns the result
int add(int a, int b)
{
int sum = a + b;
return sum; // Return the sum to the calling code
}
int main()
{
int res = add(3, 5);
cout << "The sum is: " << res << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
总结¶
条件判断是 C++ 编程中的一个重要因素,提供了对程序执行的灵活性和管理。当正确使用时,它可以提高应用程序的性能和适应性。然而,过度使用或错误管理条件判断语句可能导致代码复杂性增加、清晰度降低和安全性问题。找到平衡并正确使用这些语句对于提升代码质量至关重要。