C++ 中的跳转语句¶
跳转语句用于在某些条件满足时改变程序的执行流。它们用于终止或继续程序中的循环,或停止函数的执行。
C++ 中的跳转语句类型¶
在 C++ 中,有四种跳转语句:
breakcontinuegotoreturn
continue 语句¶
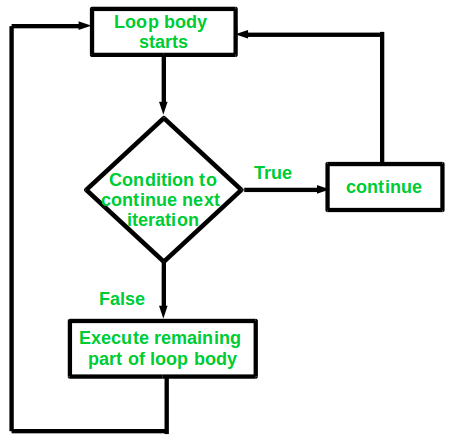
C++ 中的 continue 语句 用于跳过循环体中某些指定部分,并继续执行下一次循环迭代,而不是终止整个循环。它必须和条件判断语句一起使用,并且条件判断语句要位于循环中。
该语句可以在 for 循环、while 循环 或 do-while 循环 中使用。
continue 语法¶
continue 语句的流程图¶
continue 语句示例¶
考虑一个场景:输出 1 到 10 之间的所有数字,但跳过数字 5。此时可以在 i 为 5 时使用 continue 语句。以下是实现该功能的程序:
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// continue statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver code
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
if (i == 5)
continue;
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出
break 语句¶
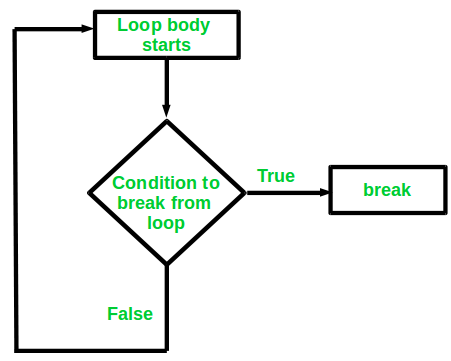
C++ 中的 break 语句 用于在条件满足时终止整个循环。与 continue 语句不同,break 语句会直接跳出循环,不再执行循环中剩余的部分。
break 语句通常与条件判断语句(如 if, if-else 或 switch 语句)配合使用,且可以在 for 循环、while 循环或 do-while 循环中使用。
语法¶
break 语句的流程图¶
break 语句示例¶
考虑一个场景:输出一系列数字,但不输出大于某个特定值 K 的数字。在这种情况下,可以在 i 为 K 时使用 break 语句。以下是实现该功能的程序:
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// break statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
// Breaking Condition
if (i == 5)
break;
cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}
Output
return 语句¶
return 语句用于将控制权从函数中返回。这比 break 更强大,它可以在函数执行结束或满足某个条件时,终止整个函数的执行。
每个函数(除了 void() 函数)都有一个 return 语句,返回一个值。虽然 void() 函数没有返回类型,但可以使用 return 语句来终止函数执行。
语法¶
return 语句示例¶
示例 1: 下面是演示 return 语句的程序。
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// return statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver code
int main()
{
cout << "Begin ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// Termination condition
if (i == 5)
return 0;
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "end";
return 0;
}
输出
解释 该程序首先打印 "Begin",然后开始循环,输出 i 的值。当 i 等于 5 时,整个函数终止,因此 "end" 语句永远不会被执行。
注意:
void()函数中的return语句可以不带任何返回类型。
示例 2: 下面的程序演示了在 void 函数中使用 return 语句:
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the return
// statement in void return type function
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to find the greater element
// among x and y
void findGreater(int x, int y)
{
if (x > y) {
cout << x << " "
<< "is greater"
<< "\n";
return;
}
else {
cout << y << " "
<< "is greater"
<< "\n";
return;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
// Function Call
findGreater(10, 20);
return 0;
}
输出
goto 语句¶
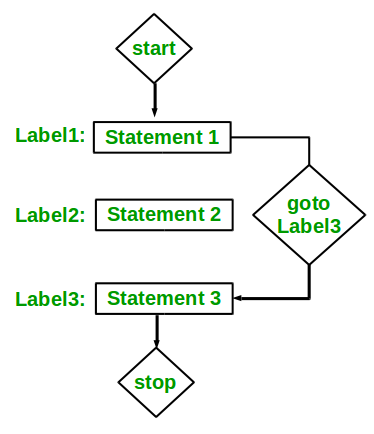
C++ 中的 goto 语句 用于跳转
到程序中的某个指定部分。每个 goto 语句都关联一个标签,程序会跳转到该标签处执行。标签可以在程序中的任何地方声明,并且不要求必须位于 goto 语句的前面或后面。
语法¶
goto 语句的流程图¶
注意: 使用
goto语句会使程序的执行流程变得难以理解,因此通常避免在程序中使用。
goto 语句示例¶
下面是一个演示 goto 语句的程序:
- C++
// C++ program to demonstrate the
// goto statement
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 4;
if (n % 2 == 0)
goto label1;
else
goto label2;
label1:
cout << "Even" << endl;
return 0;
label2:
cout << "Odd" << endl;
}
输出
解释: 该程序用于判断一个数是偶数还是奇数。如果用户输入的数字为 4,则 if 语句的条件成立,程序会跳转到 label1,并输出 "Even"。